Gut Health 101: What Your Stomach Is Trying to Tell You

Gut health basics are essential for understanding how your digestive system affects your overall well-being. Your stomach and gut send signals that can reveal much about your health, from digestion problems to immune function. This article explores the powerful messages your stomach is trying to tell you, common gut issues, and practical ways to improve gut health for a happier, healthier life.
What Is Gut Health?
Gut health refers to the balance and function of microorganisms and tissues in your digestive system, including the stomach and intestines. A healthy gut helps digest food, absorb nutrients, and protect the body from harmful bacteria.
Why Gut Health Basics Matter
Your gut is often called the “second brain” because it communicates with your brain and influences mood, immunity, and energy. Poor gut health can lead to problems like bloating, constipation, fatigue, and even mental health issues.
Common Gut Health Signals and What They Mean
Bloating and Gas: Your Gut’s Warning Sign
Bloating and excess gas can indicate food intolerances, poor digestion, or imbalanced gut bacteria.
Case Study: Bloating Linked to Food Sensitivity
Emma experienced daily bloating after meals. After testing, she discovered lactose intolerance. Removing dairy from her diet reduced symptoms significantly.
Stomach Pain and Cramping: Don’t Ignore the Warning
Pain or cramps can be caused by infections, inflammation, or conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Case Study: IBS Diagnosis After Chronic Stomach Pain
John suffered from recurring stomach cramps and diarrhea. After medical evaluation, he was diagnosed with IBS and managed symptoms through diet and stress reduction.
Constipation or Diarrhea: Signals of Imbalance
Changes in bowel habits often reflect gut imbalance, dehydration, or poor fiber intake.
Common Gut Symptoms and Possible Causes
| Symptom | Possible Cause | Suggested Action |
|---|---|---|
| Bloating | Food intolerance, poor digestion | Eliminate trigger foods, probiotics |
| Stomach pain | IBS, infection, inflammation | Medical evaluation, dietary changes |
| Constipation | Low fiber, dehydration | Increase fiber, hydrate |
| Diarrhea | Infection, food sensitivity | Hydrate, see doctor if persistent |
| Fatigue | Gut inflammation, nutrient deficiency | Balanced diet, medical check-up |
How to Improve Your Gut Health Basics

Eat a Balanced, Fiber-Rich Diet
Fiber feeds good gut bacteria and helps maintain regular bowel movements.
Include Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria found in yogurt and fermented foods. Prebiotics are fibers that feed these bacteria.
Stay Hydrated
Water supports digestion and prevents constipation.
Manage Stress
Stress negatively affects gut function and can worsen symptoms.
The Role of Gut Health in Immunity and Mental Wellness
A healthy gut supports a strong immune system and produces neurotransmitters like serotonin, influencing mood and mental health.
Case Study: Gut Health and Anxiety
Sarah struggled with anxiety and digestive issues. After improving her gut health with diet and probiotics, she noticed a significant reduction in anxiety symptoms.
When to See a Doctor
Persistent gut symptoms, unexplained weight loss, blood in stool, or severe pain require medical attention.
Additional Gut Health Tips
- Avoid excessive processed foods and sugar.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine.
- Exercise regularly to promote digestion.
- Get enough sleep to support gut repair.
The Microbiome: Your Gut’s Powerful Ecosystem
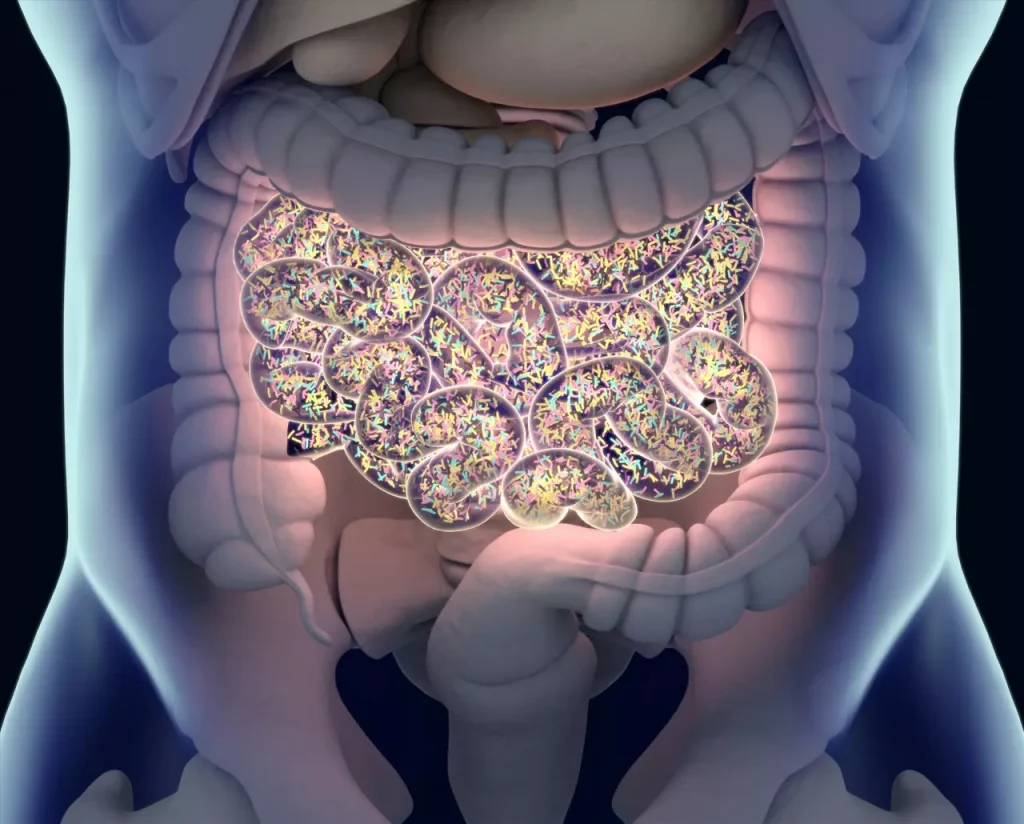
At the core of gut health basics is the gut microbiome a complex community of trillions of bacteria, viruses, and fungi living in your digestive tract. This ecosystem plays a vital role in digestion, nutrient absorption, immune function, and even mood regulation.
Why a Balanced Microbiome Matters
A diverse and balanced microbiome helps:
- Break down food efficiently
- Produce essential vitamins like B12 and K
- Protect against harmful pathogens
- Regulate inflammation
Factors That Disrupt Your Microbiome
- Antibiotic use
- Poor diet high in processed foods and sugar
- Chronic stress
- Lack of sleep
- Environmental toxins
Case Study: Restoring Microbiome Diversity
After a course of antibiotics, Lisa experienced digestive discomfort and fatigue. She improved her microbiome diversity by eating fermented foods and taking a probiotic supplement, which helped restore her gut health.
The Gut-Brain Connection: How Your Stomach Influences Your Mind
One of the most fascinating aspects of gut health basics is the gut-brain axis—a two-way communication system between your gut and brain. This connection explains why gut issues can affect mood, anxiety, and cognitive function.
How the Gut Communicates with the Brain
- Via the vagus nerve
- Through gut-produced neurotransmitters like serotonin (about 90% of serotonin is made in the gut)
- By immune system signaling
Signs Your Gut May Be Affecting Your Mental Health
- Anxiety or depression alongside digestive symptoms
- Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
- Mood swings linked to diet or gut discomfort
Case Study: Improving Mental Health Through Gut Care
Tom struggled with anxiety and frequent stomach upset. After adopting a gut-friendly diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics, he noticed improved mood stability and reduced digestive symptoms.
Food Sensitivities and Allergies: What Your Gut Is Telling You

Food sensitivities and allergies are common reasons your stomach may send distress signals. Unlike allergies, sensitivities often cause delayed and subtle symptoms, making them harder to identify.
Common Food Sensitivities
- Gluten
- Dairy
- Soy
- Eggs
- Nightshades (tomatoes, peppers)
How to Identify Food Sensitivities
- Keep a detailed food and symptom diary
- Try elimination diets under professional guidance
- Consider testing options like IgG food sensitivity tests
Managing Food Sensitivities
Avoidance of trigger foods, combined with gut healing protocols, can reduce symptoms and improve overall gut health.
The Role of Digestive Enzymes in Gut Health
Digestive enzymes are proteins that help break down food into nutrients your body can absorb. Insufficient enzyme production can cause symptoms like bloating, gas, and indigestion.
Common Digestive Enzyme Deficiencies
- Lactase deficiency leading to lactose intolerance
- Pancreatic enzyme insufficiency affecting fat and protein digestion
Supporting Digestive Enzyme Function
- Eating smaller, frequent meals
- Including enzyme-rich foods like pineapple (bromelain) and papaya (papain)
- Considering enzyme supplements if recommended by a healthcare provider
The Impact of Lifestyle on Gut Health Basics
Your daily habits significantly influence gut health. Beyond diet, factors like sleep, exercise, and stress management are crucial.
Sleep and Gut Health
Poor sleep disrupts the gut microbiome and increases inflammation, worsening digestive symptoms.
Exercise and Digestion
Regular physical activity promotes healthy bowel movements and supports microbial diversity.
Stress Management
Chronic stress alters gut motility and microbiota balance, often worsening symptoms like IBS.
Lifestyle Factors and Their Effects on Gut Health
| Lifestyle Factor | Positive Effect on Gut Health | Negative Effect on Gut Health |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | High fiber, fermented foods | Processed foods, high sugar intake |
| Sleep | 7-9 hours of quality sleep | Sleep deprivation, irregular patterns |
| Exercise | Moderate, regular physical activity | Sedentary lifestyle |
| Stress Management | Mindfulness, relaxation techniques | Chronic stress, anxiety |
| Medication Use | Responsible use under medical guidance | Overuse of antibiotics, NSAIDs |
When Gut Symptoms Indicate a Serious Condition
Sometimes, stomach signals may point to serious health issues requiring prompt medical attention.
Warning Signs to Watch For
- Persistent severe abdominal pain
- Blood in stool or black, tarry stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation lasting weeks
Common Serious Gut Conditions
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis)
- Celiac disease
- Gastrointestinal infections
- Stomach ulcers
Practical Gut Health Tips for Everyday Life
- Eat a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables daily.
- Incorporate fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut.
- Stay hydrated with water and herbal teas.
- Avoid excessive alcohol and caffeine.
- Manage stress through yoga, meditation, or hobbies.
- Get regular exercise and prioritize sleep.
The Role of Hydration in Maintaining Gut Health Basics
Proper hydration is a fundamental but often overlooked aspect of gut health basics. Water plays a critical role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and maintaining the delicate balance of your gut microbiome.
How Hydration Supports Your Gut
- Aids digestion: Water helps dissolve nutrients and soluble fiber, allowing them to pass smoothly through the digestive tract.
- Prevents constipation: Adequate hydration softens stool, making bowel movements easier and reducing strain.
- Maintains mucosal lining: The gut lining requires moisture to function properly and protect against harmful bacteria.
- Supports microbiome balance: Dehydration can disrupt the environment where beneficial bacteria thrive.
Signs Your Gut May Be Dehydrated
- Constipation or hard stools
- Bloating and discomfort
- Fatigue and headaches linked to poor digestion
Practical Hydration Tips for Gut Health
- Aim to drink at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
- Include hydrating foods like cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges in your diet.
- Limit excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can dehydrate the body.
- Start your day with a glass of water to kickstart digestion.
Case Study: Hydration Improving Digestive Health
After struggling with chronic constipation and bloating, David increased his daily water intake and added hydrating fruits to his meals. Within weeks, his digestion improved, and he experienced less discomfort.
The Importance of Sleep for Gut Health Basics
Sleep is a vital component of gut health basics that is often underestimated. Quality sleep supports the repair and regeneration of the gut lining, regulates gut bacteria, and helps maintain overall digestive health.
How Sleep Affects Your Gut
- Gut lining repair: During deep sleep, the body repairs the intestinal lining, preventing leaks and inflammation.
- Microbiome balance: Poor sleep disrupts the diversity and function of gut bacteria, which can lead to digestive issues.
- Hormonal regulation: Sleep regulates hormones like cortisol and melatonin that influence gut motility and immune responses.
- Stress reduction: Adequate sleep lowers stress levels, which positively impacts gut function.
Consequences of Poor Sleep on Gut Health
- Increased risk of gut inflammation and disorders such as IBS.
- Higher likelihood of food sensitivities and poor nutrient absorption.
- Greater susceptibility to infections due to weakened immunity.
Tips for Improving Sleep to Support Gut Health
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time daily.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal your body it’s time to rest.
- Limit screen time and exposure to blue light at least an hour before bed.
- Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.
- Keep your sleeping environment cool, dark, and quiet.
Case Study: Sleep Improvement Enhancing Gut Health
Maria, who suffered from frequent digestive discomfort and poor sleep, adopted better sleep hygiene practices. After a few weeks, her gut symptoms lessened, and she reported feeling more energized and balanced.
Conclusion
Understanding gut health basics helps you listen to your stomach’s signals and take action before problems worsen. By adopting healthy habits and recognizing warning signs, you can improve digestion, boost immunity, and enhance overall wellness.